 |
CHAMÄLEON + ONJALA OBSERVATORY DeepSky | SITEMAP HOME CHAMÄLEON |
|
 |
|||
| « zurück zur Startseite
galaktische Nebel « back to home galactic nebula |
Großes Bild laden - load large image 2048 x 1400 Pixel Aufnahmedaten Image data |
The cometary globule CG 4 and the galaxy PGC 21338 in the constellation of Puppis.
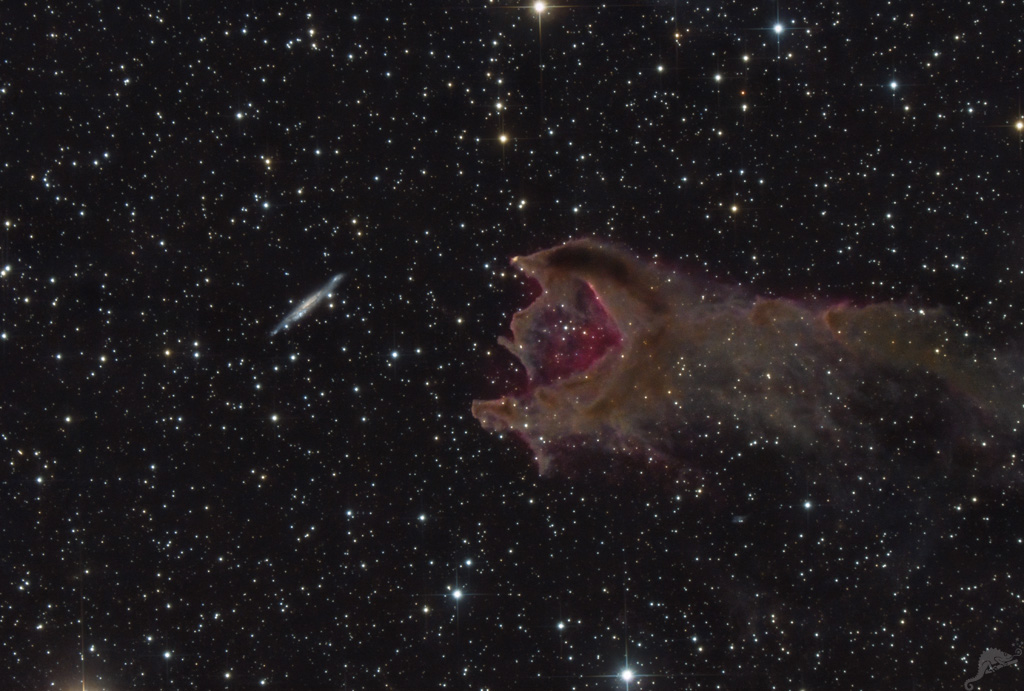

Die kometare Globule CG 4 (GN 07.29.8.01) im Zentrum des Bildes trägt auch die Eigennamen "Das Maul der Bestie" oder auch "Gottes Hand". Sie gehört zu einer Reihe von länglichen, kometenartig geformten Objekten im riesigen Gebiet des Gum-Nebels. Die Globulen besitzen einen dichten, staubigen "Kopf" und einen "Schweif" der vom Vela Supernova Überrest im Zentrum des Gum-Nebels weg zeigt. Zur Zeit werden zwei mögliche Erklärungen für die Entstehung dieser Objekte diskutiert. Einerseits kann die Supernova-Explosion für die Form der Globulen verantwortlich sein, andererseits auch die Strahlung von heißen, neu entstandenen Sternen in der Region.
Die Molekülwolke enthält genug Material für mehrere Sterne und sehr wahrscheinlich findet im Inneren eine aktive Sternentstehung statt. Der "Kopf" der Globule hat einen Durchmesser von etwa 1,5 Lichtjahren und liegt etwa 1300 Lichtjahre vom Sonnensystem entfernt.
Die Galaxie PGC 21 338 (ESO 257-19) ist mit einer Entfernung von etwa 110 Millionen Lichtjahren viel, viel weiter vom Sonnensystem entfernt als CG 4. Sie wird als Balkenspirale (SB c) klassifiziert und ist mit einer Galaxien-Leuchtkraft von 30 Milliarden Sonnen in ihrer Größe etwa mit unserer Milchstraße vergleichbar. Ihre scheinbare Größe am Himmel liegt bei nur 2,6 x 0,5 Bogenminuten, die visuelle Helligkeit beträgt 14m5.
Object description
The cometary globule CG 4 (GN 07.29.8.01) in the centre of our image also shares the proper names "The Mouth of the Beast" or "God's Hand". It belongs to a series of elongated, comet-like objects in the huge area of the Gum Nebula. The globules have a dense, dusty "head" and a "tail" pointing away from the Vela Supernova remnant in the centre of the Gum Nebula. Two possible explanations for the formation of these objects are currently being discussed. On the one hand, the supernova explosion may be responsible for the shape of the globules, on the other hand, radiation from hot, newly formed stars in the region.
The molecular cloud contains enough material for several stars and probably active star formation is taking place inside. The "head" of the globule has a diameter of about 1.5 light years and lies about 1300 light years from the solar system.
 |
The galaxy PGC 21 338 (ESO
257-19), at a distance of about 110 million light-years, is much, much further
from the Solar System than CG 4. It is classified as a barred spiral and, with
a galaxy luminosity of 30 billion Suns, is roughly comparable in size to our
Milky Way. We show a wide-angle view of the region here. Detailed information on CG 4 is provided by ESO here. Eine Weitwinkelansicht der Region zeigen wir hier. Detaillierte Informationen zu CG 4 gibt die ESO hier. « Hier oder auf das Vorschaubild zum Laden eines großen Bildes mit Objektbezeichnungen und Größenvergleich zum Mond klicken « Click here or on the thumbnail to load a large image with object annotations. |
The cometary globule CG 4 and the galaxy PGC 21338 in the constellation of Puppis.
Image data
24.-27.04.2022 - 52 x 600 s, Canon EOS 700 DA (cooled)
Telescope: Planewave CDK 12.5 with Televue 0.8x Reducer at f = 2030 mm
Location: Chamäleon Observatory, Onjala Lodge, Namibia
Image acquisition and processing: Nebulosity, StarTools, Starnet++, Photoshop
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Sonne | Mond | Sonnensystem | DeepSky | Weitwinkel | Verschiedenes | Spez. Projekte |