 |
CHAMÄLEON + ONJALA OBSERVATORY DeepSky | SITEMAP HOME CHAMÄLEON |
|
 |
|||
| « back to overview Nebula | Load higher resolution (1800 x 1200 Pixel 3500 x 2300 Pixel) | Object description |
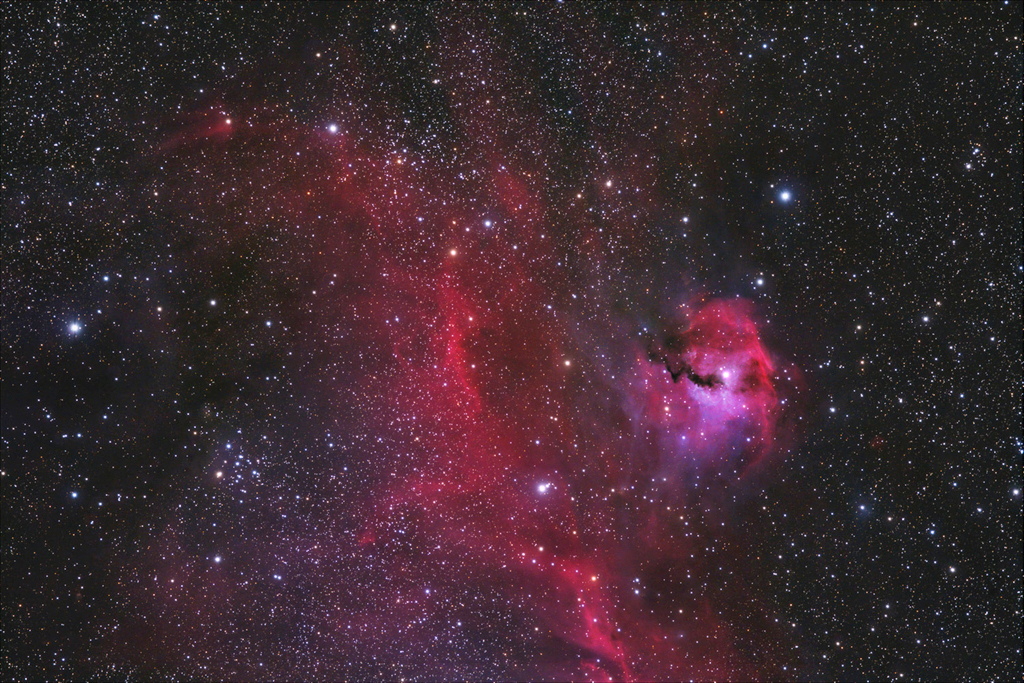

IC 2177
IC 2177 is the center of a large H-II star formation region, mixed with blue reflection nebulae. It is an approximately circular structure, roughly centered around the Be star HD 5336, which is also called Seagull Nebula because of its coarse shape. In the image orientation of our wide angle view, the seagull flies towards the lower edge of the image, whereby the approximately circular nebula structure below the wings corresponds to the head of the seagull.
The bright "head of the seagull", IC 2177, is also classified as GUM 1, Sh2-292 and vdB 93, it is a combination of reflection and emission nebulae. The hot, young B0 star HD 53367 is the source of the emission stimulation. HD 53367 is 20 times as massive as our Sun with a companion of 5 solar masses orbiting the main star on a strongly elliptical orbit The entire Gull Nebula is part of the Majoris OB1 association and is located at a distance of about 3750 light years from the solar system. IC 2177 lies along the border between the constellations Monoceros and Canis Major.
The entire Gull Nebula is part of the Majoris OB1 association and is located at a distance of about 3750 light years from the solar system. IC 2177 lies along the border between the constellations Monoceros and Canis Major.
NGC 2343 and NGC 2335
NGC 2343 is an open star cluster in the constellation Unicorn (Monoceros). It has an apparent diameter of 6 arc minutes, visually about 20 stars are observable. According to Trumpler it is classified as type III 3 p n, the distance to the solar system is estimated at 3400 light years.
NGC 2343 was discovered on 10 January 1785 by Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel. NGC 2335 is also an open star cluster in the constellation Unicorn. According to Trumpler it is classified as type III 3 m, visually about 35 stars are visible. The distance to the solar system is about 4500 light years. The star cluster was discovered on January 10, 1785 by Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel.
 |
Further Objects PK 223-2.1 is probably a very faint planetary nebula of about 80 arcseconds in diameter. vdB 91 is a faint reflection nebula of about 60 arcseconds diameter. « The annotated image shows the size comparison with the moon. Collinder 445 und 446 Only the following data can be found for these two star clusters: Collinder 445 is a small open star cluster with an apparent diameter of 5 arc minutes. It contains about 30 stars of the 12th magnitude and fainter. Collinder 446 is smaller than Collinder 465 with an apparent diameter of 4 arcminutes and contains about 25 stars at an apparent magnitude 11 magnitude magnitude |
Per Collinder was a Swedish astronomer at Lund Observatory who was researching the structure of open star clusters and their spatial distribution in the Milky Way. In 1931 he compiled a catalogue of open star clusters, listing 471 such objects. Detailed information about Per Collinder and the complete catalogue can be found here.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Sun | Moon | Solar System | DeepSky | Widefield | Miscellaneous | Spec. Projects |